Intro
originally published on wordpress.com
This is a demonstration of how to use a real time clock with Arduino.
This can be helpful when making clocks as well as keeping logs of events.
Parts
- Arduino Uno (or similar)
- RTC module (eBay / SparkFun: ds1307 RTC module
- some tactile switches for the adjustment push-buttons
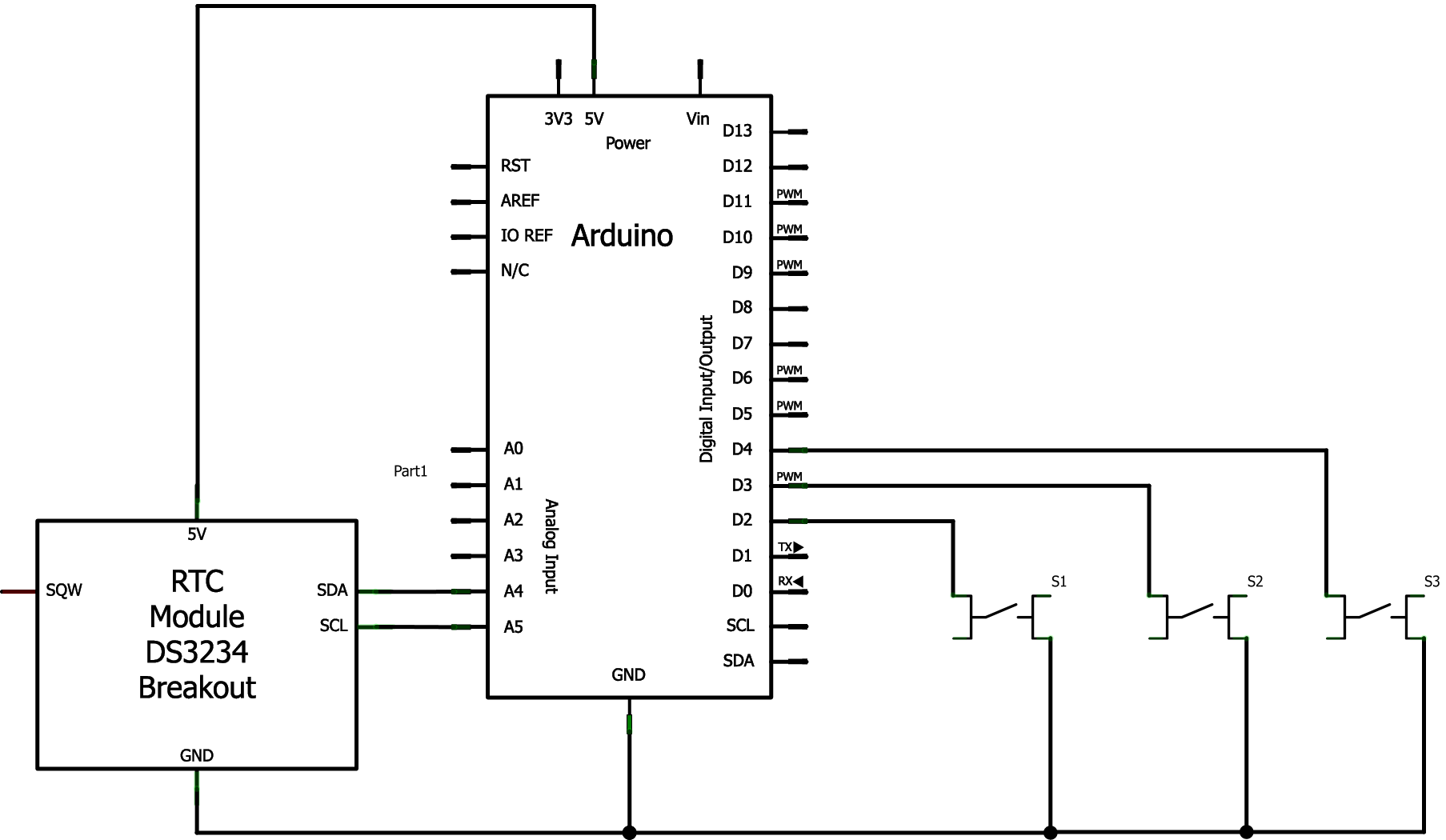
Circuit
I planned what I did using Fritzing Note: The switches don't have pull up resistors as I utilised the internal pull up resisters of the digital Arduino pins.
Here is the Fritzing schematic:
Here is the Fritzing virtual breadboard layout:
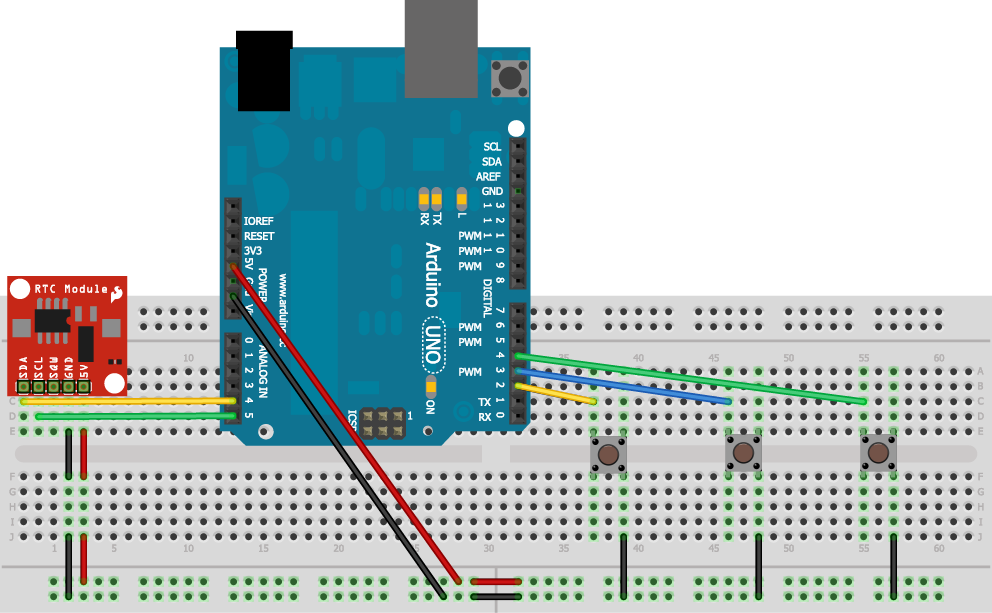
Here is the actual circuit on a breadboad:

Once implemented, and the code is on the Arduino, if the Serial Monitor is opened you should see something like this:

This is handy as the buttons allow for the adjustment of time on the RTC by using an on-board time variable as an intermediary step.
The source code below is commented and should help further.
#include <Time.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <DS1307RTC.h> // a basic DS1307 library that returns time as a time_t
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // start the serial connectio
n to the PC.
pinMode(2, INPUT); // set pin 2 as an input
digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // activate internal pullup resistor on pin 2
pinMode(3, INPUT); // set pin 3 as an input
digitalWrite(3, HIGH); // activate internal pullup resistor on pin 3
pinMode(4, INPUT); // set pin 4 as an input
digitalWrite(4, HIGH); // activate internal pullup resistor on pin 4
setSyncProvider(RTC.get); // the function to get the time from the RTC
setSyncInterval(60); // set the number of seconds between re-sync
if(timeStatus()!= timeSet)
Serial.println("Unable to sync with the RTC.");
else
Serial.println("RTC has been read.");
}
void loop()
{
if (digitalRead(2) == LOW) { // Zero the minutes!
// setting the onboard time to 0 minutes.
setTime(hour(),0,second(),day(),month(), year());
RTC.set(now()); // sending the onboard time to the RTC.
Serial.println("Minutes Reset."); // send confirmation to the PC.
}
// *** had to adjust the adjustTime function in the Time library.
// Inside Time.cpp, the adjustTime method was replaced with:
//
// void adjustTime(long adjustment){
// setTime(sysTime + adjustment);
// }
//
if (digitalRead(3) == LOW) { // add an hour!
adjustTime(3600); // adjust onboard time by +3600 seconds (1hr) ***
RTC.set(now()); // sending the onboard time to the RTC.
Serial.println("Added an hour."); // send confirmation to the PC.
}
if (digitalRead(4) == LOW) { // add a minute!
adjustTime(60); // adjust onboard time by +60 seconds (1min) ***
RTC.set(now()); // sending the onboard time to the RTC.
Serial.println("Added a minute."); // send confirmation to the PC.
}
// this section is for setting the rtc chip from the serial terminal.
if(Serial.available()){
time_t t = processSyncMessage();
if(t >0)
{
RTC.set(t); // set the RTC and the system time to the received value
setTime(t);
}
}
digitalClockDisplay(); // sends an update of the time to the PC.
delay(1000); // wait for a bit.
}
void digitalClockDisplay(){
// digital clock display of the time over serial
Serial.print(hour());
Serial.print(":");
printDigits(minute());
Serial.print(":");
printDigits(second());
Serial.println();
}
void printDigits(int digits){
// utility function for digital clock display: prints preceding colon and leading 0
if(digits < 10)
Serial.print('0');
Serial.print(digits);
}
/* code to process time sync messages from the serial port */
#define TIME_MSG_LEN 11 // time sync to PC is HEADER followed by unix time_t as ten ascii digits
#define TIME_HEADER 'T' // Header tag for serial time sync message
time_t processSyncMessage() {
// return the time if a valid sync message is received on the serial port.
while(Serial.available() >= TIME_MSG_LEN ){ // time message consists of a header and ten ascii digits
char c = Serial.read() ;
Serial.print(c);
if( c == TIME_HEADER ) {
time_t pctime = 0;
for(int i=0; i < TIME_MSG_LEN -1; i++){
c = Serial.read();
if( c >= '0' && c <= '9'){
pctime = (10 * pctime) + (c - '0') ; // convert digits to a number
}
}
return pctime;
}
}
return 0;
}